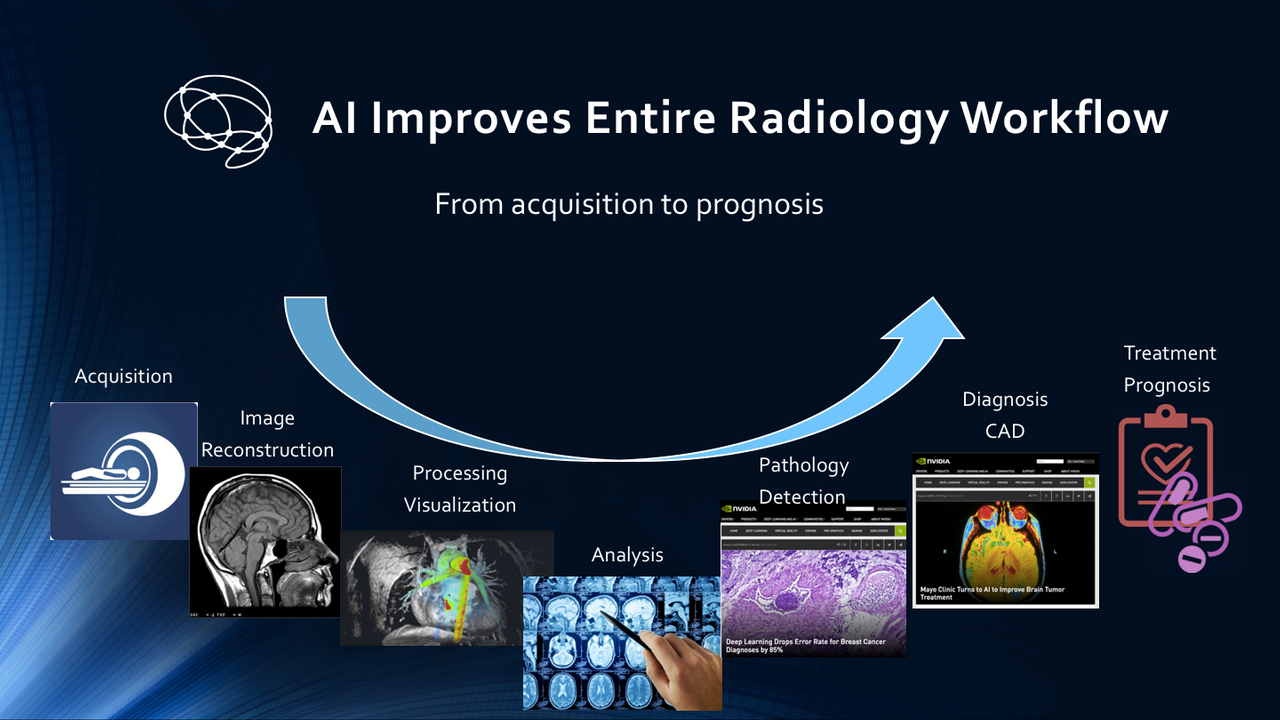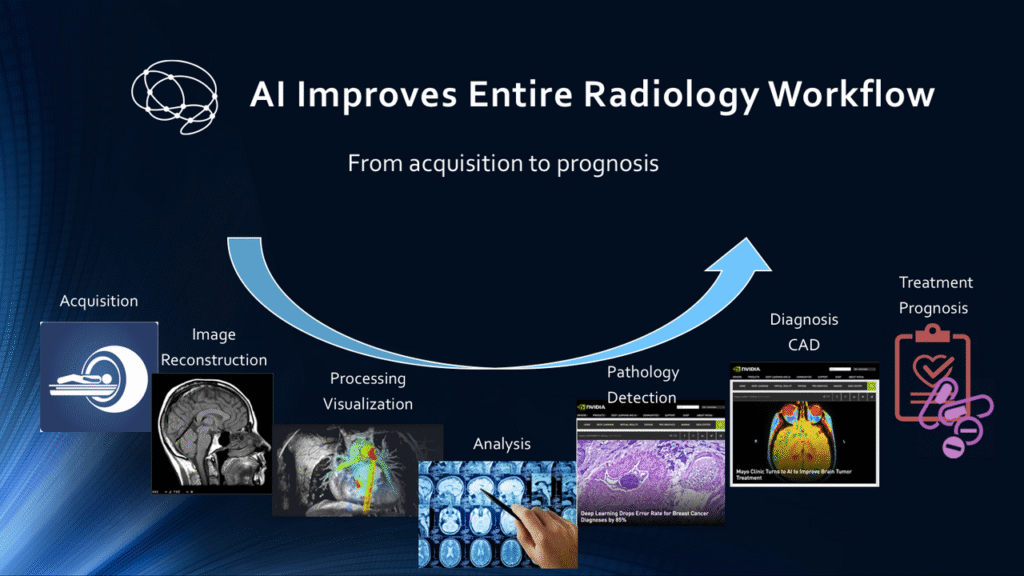
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is making powerful strides in the field of radiology, promising to detect diseases faster, more accurately, and at a lower cost than ever before. With algorithms now capable of reading X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, the question is no longer whether AI can assist in radiology—but whether it might eventually replace human radiologists altogether.
The truth lies in a more nuanced middle ground: while AI is transforming diagnostic imaging, it is not poised to fully replace the trained expertise and contextual judgment of radiologists anytime soon. Instead, it is reshaping the profession and enhancing human capabilities.
The Role of AI in Radiology Today
AI is already being used in many radiology departments worldwide. Key applications include:
- Image Analysis: Identifying tumors, fractures, hemorrhages, or infections in medical images with remarkable speed.
- Workflow Optimization: Prioritizing urgent cases in scan queues and automating repetitive reporting tasks.
- Quantitative Imaging: Measuring disease progression or treatment response through automated tracking.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting patient outcomes based on image patterns and clinical data.
How AI Compares to Human Radiologists
| Capability | AI Performance | Radiologist Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Instantaneous after deployment | Several minutes per image | AI is faster |
| Accuracy (in some tasks) | Equal or superior in narrow domains | High with context awareness | Comparable, varies by task |
| Contextual Reasoning | Limited | Strong (includes patient history) | Radiologists superior |
| Pattern Recognition | Excellent on trained patterns | Excellent with experience | AI excels at repetition |
| Adaptability | Needs retraining | Learns and adjusts continuously | Humans more flexible |
| Empathy & Communication | None | High, crucial in patient care | Human-exclusive skill |
Major Advancements in AI Radiology Tools
- Deep Learning Models: Trained on millions of annotated scans, these systems can detect lung nodules, brain bleeds, and more with high precision.
- Computer-Aided Detection (CAD): Earlier versions helped flag anomalies, but modern versions are now standalone detectors.
- Multi-Modality Integration: AI can now combine CT, MRI, and lab data to improve diagnostic confidence.
- Automated Reporting: Natural Language Generation (NLG) systems generate structured radiology reports based on AI findings.
Opportunities and Benefits
- Increased Efficiency: AI can screen routine cases, allowing radiologists to focus on complex or ambiguous ones.
- Better Accessibility: In underserved areas lacking radiologists, AI tools offer much-needed diagnostic support.
- Consistency: AI doesn’t suffer from fatigue or distraction, maintaining constant performance.
- Faster Turnaround Time: Results can be delivered in seconds, reducing patient anxiety and expediting treatment.
Key Concerns and Limitations
- Bias in Training Data: AI models trained on biased or incomplete datasets may perform poorly on diverse populations.
- Over-Reliance on Technology: Blind trust in AI results without human oversight can be dangerous.
- Lack of Interpretability: Many models operate as “black boxes,” with little insight into how conclusions are reached.
- Legal and Ethical Liability: Who is responsible if an AI misdiagnosis leads to harm—the software developer, the hospital, or the physician?
- Integration Challenges: Existing hospital IT systems often struggle to incorporate AI tools seamlessly.
The Future of Radiology: Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing radiologists, AI is expected to become a digital colleague—a powerful assistant that enhances decision-making. The future model is likely to be radiologist + AI, where:
- AI handles image triage and routine interpretation.
- Radiologists verify findings, contextualize results, and communicate with patients and clinicians.
- The combination leads to higher accuracy, faster diagnosis, and better patient outcomes.
Overview Table: AI vs. Radiologist Roles
| Function | AI Role | Human Radiologist Role |
|---|---|---|
| Image Triage | Sorts and flags urgent scans | Confirms urgency and provides treatment plan |
| Routine Diagnosis | Detects common conditions | Validates, adjusts based on full context |
| Complex Case Interpretation | Limited | Strong contextual and interdisciplinary insight |
| Communication | Not capable | Discusses findings with doctors/patients |
| Ethics & Judgment | Absent | Applies medical ethics and clinical judgment |
| Final Decision | Supportive only | Ultimately accountable |
3 Best One-Line FAQs
Q1: Can AI fully replace radiologists in the future?
Not likely—AI can assist but lacks the contextual reasoning, empathy, and adaptability of human radiologists.
Q2: Is AI more accurate than radiologists?
In some specific tasks, yes—but human oversight is still essential for holistic diagnosis and patient safety.
Q3: How is AI being used in radiology today?
AI aids in image analysis, triage, reporting, and predictive analytics to speed up and support diagnosis.
Conclusion
The narrative of “AI vs. Radiologists” is evolving into “AI and Radiologists.” Machines can process massive data volumes, detect patterns with razor-sharp accuracy, and never tire—but only humans can interpret findings in the context of a patient’s history, explain results, and make nuanced ethical decisions.
The future of radiology is not about replacement but reinforcement. Those who embrace AI as a partner rather than a competitor will be at the forefront of a smarter, faster, and more human-centered medical future.